Today, almost every other electronic appliance, mechanical parts, toys, and food containers are manufactured from hard plastics. Hence the tendency of you finding plastics in your everyday items is high, especially in goods from automobiles, motorbikes, and clothing.
Why is plastic being used so widely?

Plastic is available at a low cost. It’s a versatile material that can be molded to form virtually any shape, and that’s the reason manufacturers prefer it. Unfortunately, hard plastics can be easily damaged, and in fact, some lower quality plastics may degrade when exposed to harsh weather conditions.
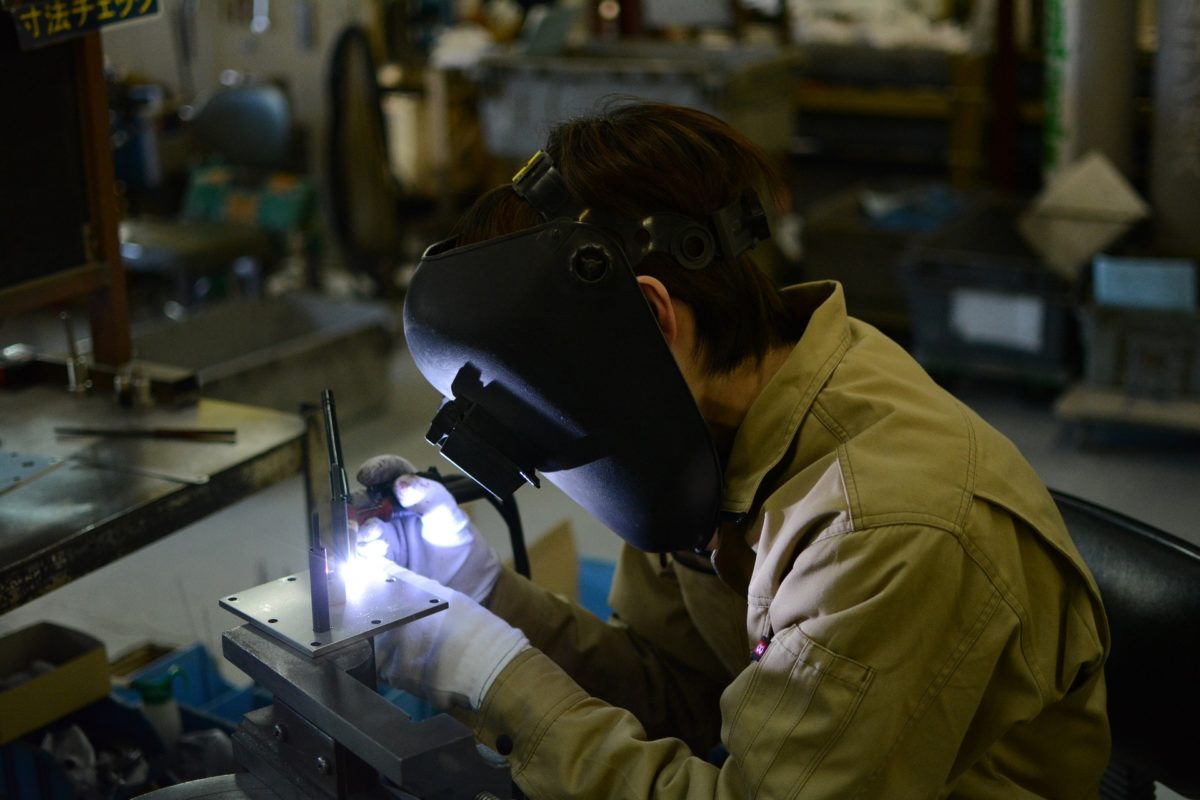
Mostly when plastic cracks or breaks, it’s thrown away. However, many people don’t realize that it’s also possible to weld plastic. Let’s answer some frequently asked questions on plastic welding:
What is Plastic Welding?
According to experts, Plastic welding is the process of creating a molecular bond between two compatible thermoplastics.
Welding as a whole is capable of providing superior strength and also drastically reduce cycle times to mechanical joining and chemical bonding.
Welding of plastics is of functional importance in several automotive, pharmaceutical and electronic packaging applications. Moreover, there have been advancements in textile joining and dissimilar materials (e.g. plastics to ceramics or metals).
What are the best ways to weld plastic?
Plastic can be welded with numerous welding processes. Here’s a brief description of the significant ones:
- Friction Welding: This form of welding employs friction to generate heat and fuse the two-part pieces. Commonly used in the automotive and aviation industries for joining plastics with metals.
- Hot Gas Welding: A heat gun is used to soften the two pieces along with a filler rod. It’s commonly utilized to create small plumbing fittings, water tanks, and other industrial equipment.
- Laser Welding: The most ‘high-tech’ way of repairing or joining plastics. The laser beam helps in joining the two pieces. The process is quick and delivers exact control.
- Solvent Welding: Commonly used for joining ABS and PVC pipes in household plumbing, this process utilizes solvents such as tetrahydrofuran and dichloromethane to merge the chains of the two pieces.
Why is heat used in plastic welding?
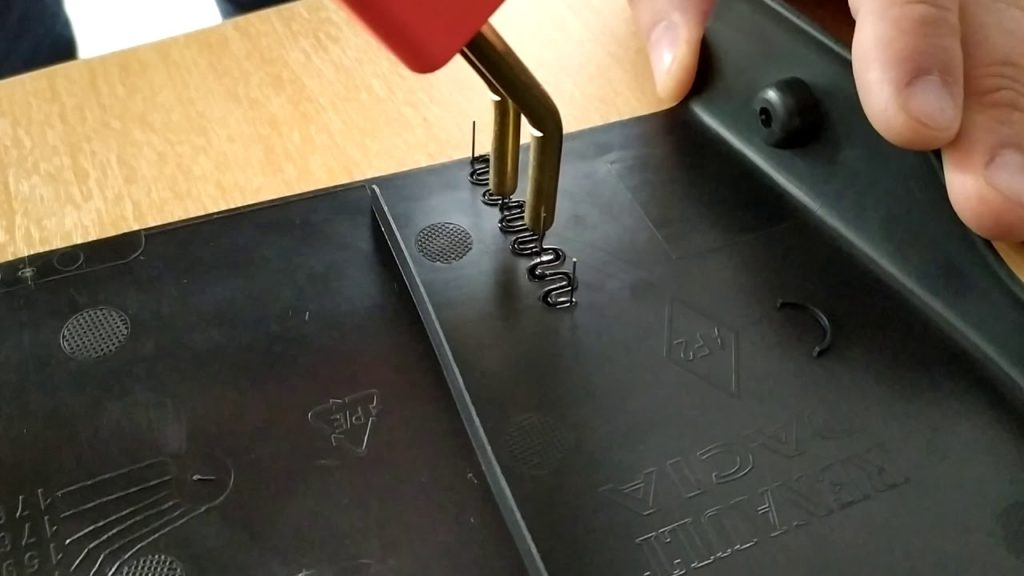

Because the plastic welding process must form a melt layer at the faying surface to allow intermolecular diffusion for the formation of a molecular bond.
As if it’s in the solid-state, polymer chains will not flow. Hence, the joint surfaces of both parts must be melted to allow the plastic molecules to quickly diffuse across the interface and bond with the fragments of the subsequent part.
In plastic welding, the hotter the melt, the higher the molecular movement. As a result, the weld can be made quickly with a shorter cycle time.
What is an ultrasonic welding machine?
One of the most common processes to weld plastics is ‘ultrasonic.’
The process works through the translation of the Alternative Current (AC) into mechanical vibrations using piezoelectric ceramics. The vibrations generated are then passed through the part towards the joint, where they cause stress and strain in the contact area between two parts, which further leads to localized heating and melting of the polymer.
Ultrasonic welding machines typically offer a weld time from one-tenth to two seconds.
We hope this blog helped in answering your query on plastic welding!